Physiotherapy is a healthcare profession that focuses on improving movement and function, reducing pain, and helping individuals recover from injuries or manage chronic conditions. It involves various treatment techniques such as exercises, manual therapy, heat and cold treatments, electrical stimulation, and patient education. While physiotherapy offers numerous benefits, it also has some potential drawbacks depending on individual circumstances. In this blog, we will explore both the advantages and disadvantages of physiotherapy, providing a balanced perspective for those considering it as a treatment option.
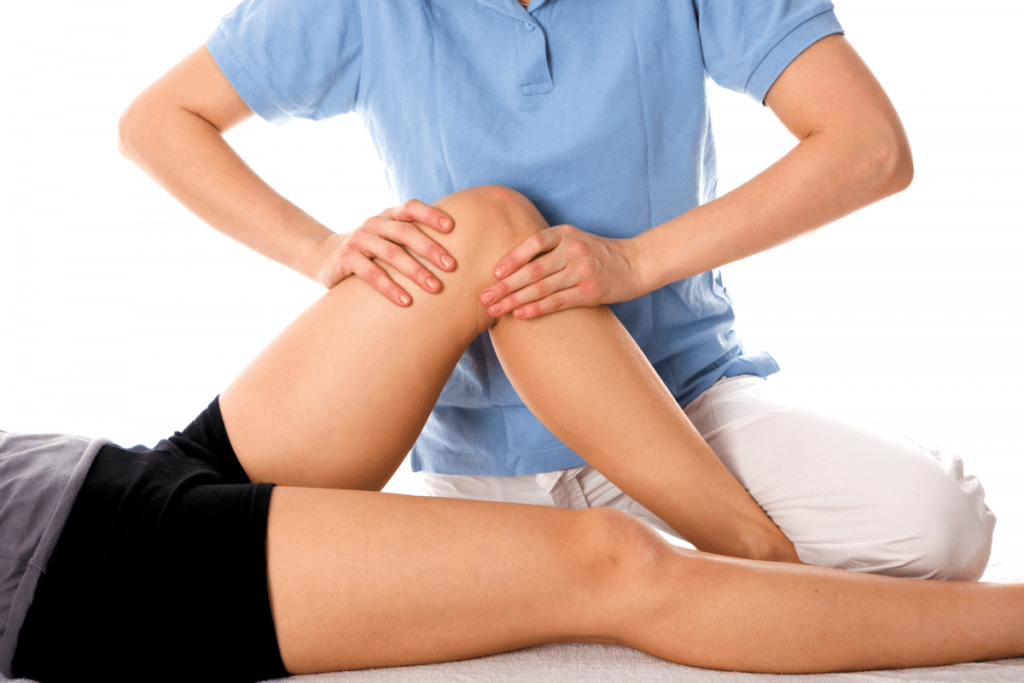

Advantages of Physiotherapy
1. Pain Relief
One of the most significant advantages of physiotherapy is its ability to help alleviate pain, whether it’s caused by an injury, surgery, or a chronic condition. Physiotherapists use various techniques such as manual therapy, hot and cold compresses, ultrasound therapy, and TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) to reduce pain and promote healing. Unlike medications, physiotherapy addresses the root cause of pain and helps individuals manage discomfort over time, potentially reducing the need for painkillers and preventing dependence on them.
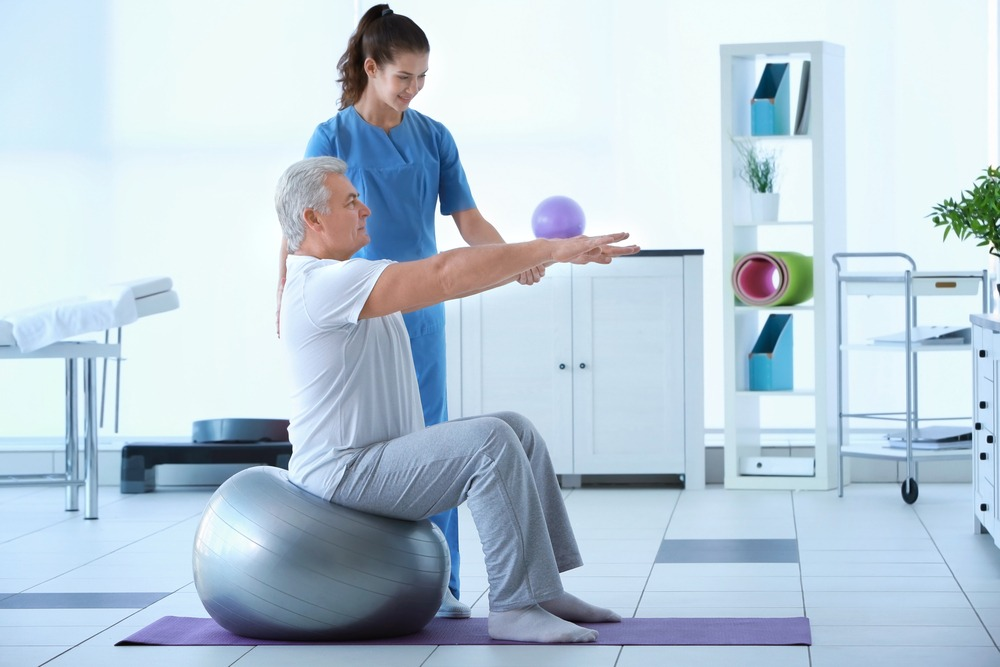

2. Improved Mobility and Function
Whether recovering from an injury or surgery, physiotherapy is designed to help individuals regain or improve their range of motion, strength, and flexibility. For example, physiotherapists may use stretching exercises, strengthening routines, and mobility techniques to help restore normal function to joints and muscles. Physiotherapy also helps prevent muscle atrophy and joint stiffness, which can occur if a person has been immobile for a long period due to injury or surgery.
By improving mobility and function, physiotherapy enhances the patient’s ability to carry out daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or even driving, ultimately improving quality of life and independence.
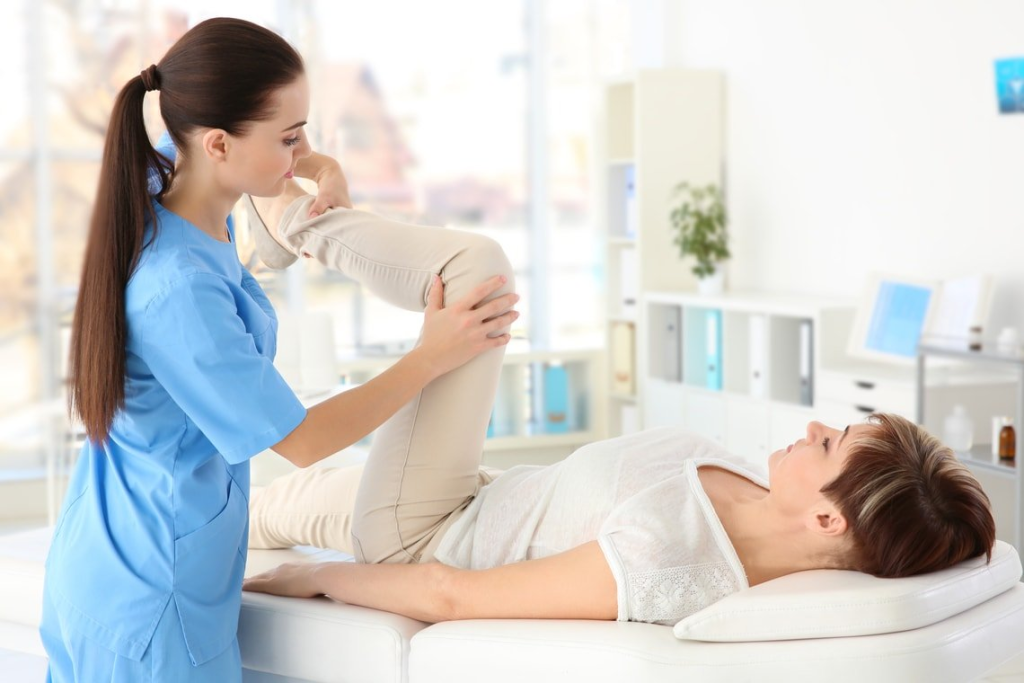

3. Prevention of Future Injuries
A key aspect of physiotherapy is injury prevention. Physiotherapists assess a patient’s posture, movement patterns, and muscle imbalances, then provide targeted exercises and techniques to address any weaknesses or abnormal movements. Correcting these imbalances and strengthening the body can reduce the risk of future injuries.
For example, athletes often benefit from physiotherapy as it can help prevent sports-related injuries by teaching proper techniques, providing strength-building exercises, and ensuring that the body is balanced and prepared for high-impact activities.
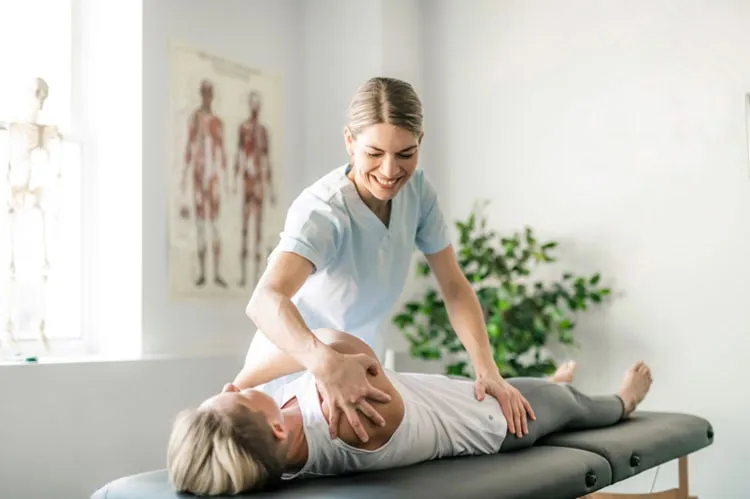

4. Management of Chronic Conditions
Physiotherapy is highly beneficial for individuals with chronic conditions such as arthritis, back pain, osteoporosis, or fibromyalgia. For chronic conditions, physiotherapy focuses on pain management, maintaining joint health, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall function. Physiotherapists provide ongoing support to help individuals manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life, often with an emphasis on self-management techniques.
For example, in patients with osteoarthritis, physiotherapists can teach them how to protect their joints, manage pain, and improve mobility through specific exercises and lifestyle adjustments.
5. Improved Posture and Alignment
Many people suffer from poor posture due to extended sitting, poor ergonomics, or improper body mechanics. Over time, this can lead to discomfort, back pain, neck pain, and muscle imbalances. Physiotherapists are trained to assess posture and provide treatment that promotes proper alignment. They may suggest corrective exercises, posture-awareness techniques, and ergonomic modifications to help improve posture and reduce the strain on the body’s muscles and joints.
Improving posture can lead to significant long-term benefits, such as reduced pain and fatigue, greater energy levels, and enhanced physical performance.
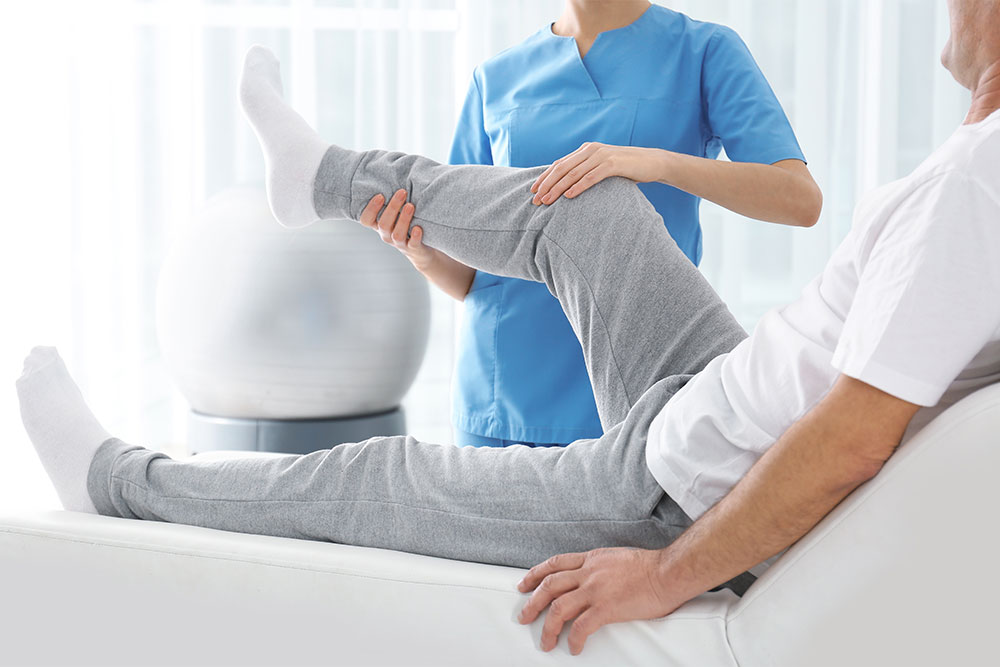

6. Holistic Approach to Treatment
Unlike other medical interventions that may focus on symptom management, physiotherapy takes a more holistic approach to treatment. Physiotherapists not only treat the physical symptoms but also work with patients to understand the broader context of their health, including their lifestyle, activity levels, and psychological well-being. This holistic approach helps to address underlying causes of pain or discomfort, such as poor posture or muscle weakness, rather than merely masking the symptoms.
Moreover, physiotherapists educate patients on the importance of self-care, exercise, and lifestyle adjustments, which encourages long-term health benefits and helps prevent future problems.
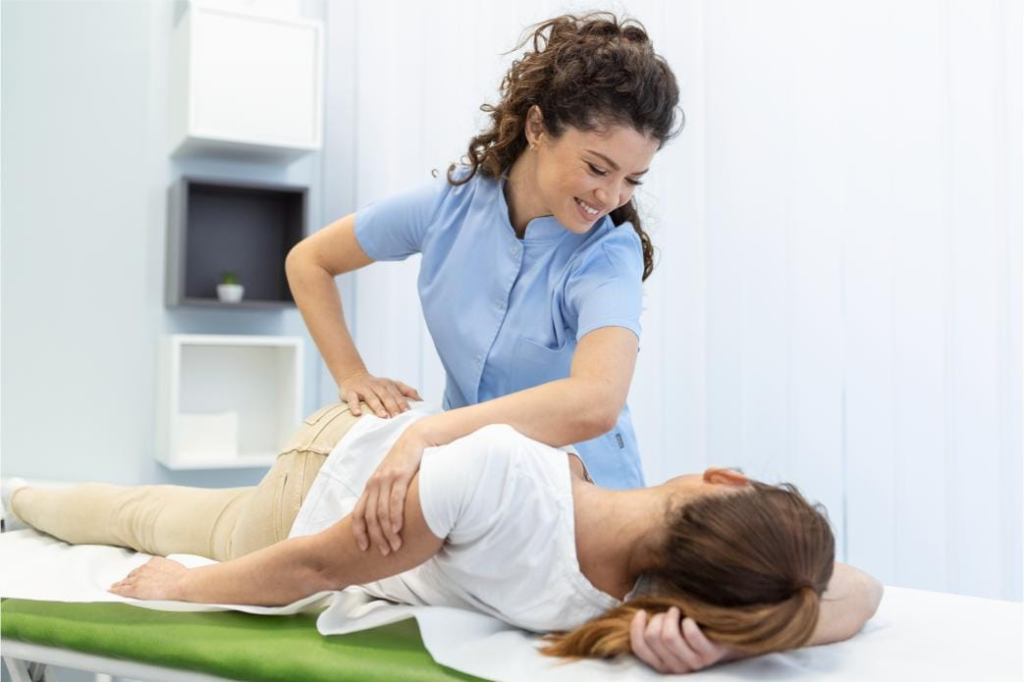

7. Non-Invasive Treatment
Physiotherapy is a non-invasive treatment option, making it an attractive alternative to surgery or medications. For individuals who want to avoid surgery or drug dependence, physiotherapy offers a natural and safe approach to recovery. In many cases, physiotherapy can help avoid the need for surgery, particularly in conditions like musculoskeletal injuries or chronic pain syndromes.
Even after surgery, physiotherapy can play a crucial role in rehabilitation, speeding up recovery time and restoring normal function without the need for additional invasive procedures.
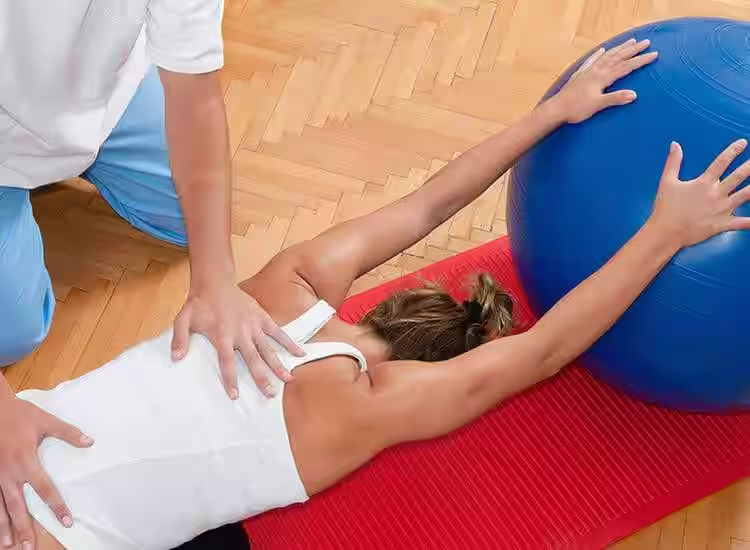

8. Improved Mental Health and Well-being
Physical health and mental health are interconnected, and physiotherapy can have a positive impact on mental well-being. Exercise, which is a key component of physiotherapy, has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, increase endorphins (the body’s natural “feel-good” chemicals), and improve overall mood. As patients recover physically and regain mobility, they also experience an improvement in their confidence and sense of control over their bodies.
Additionally, physiotherapy sessions often involve one-on-one time with the therapist, allowing patients to express concerns, gain encouragement, and develop a sense of trust and support throughout their recovery process.
Disadvantages of Physiotherapy
While physiotherapy offers many benefits, there are also some potential disadvantages or limitations to consider before committing to treatment.
1. Time-Consuming
Physiotherapy can be a time-intensive treatment option. In order to see results, patients often need to attend multiple sessions over an extended period of time. For some individuals, especially those with busy schedules, committing to frequent therapy sessions may be challenging. Additionally, the time spent on exercises at home or after each session can add up, and consistency is key to achieving the desired outcomes.
If patients miss appointments or fail to complete their prescribed exercises, progress may be slower or less effective, which can lead to frustration.

2. Discomfort or Pain During Treatment
While physiotherapy aims to reduce pain, it is not uncommon for patients to experience discomfort or mild pain during certain treatments or exercises. Techniques such as manual therapy (e.g., joint mobilizations or deep tissue massage) or stretching can occasionally lead to temporary discomfort, especially if muscles and joints are tight or injured.
Although this discomfort is often part of the healing process, it can be discouraging for some patients, particularly those who are sensitive to pain or have low pain tolerance. However, it’s important to note that physiotherapists strive to tailor treatment to the individual’s comfort level and will adjust techniques if pain becomes too severe.
3. Potential for Incomplete Results
While physiotherapy can significantly improve movement, function, and pain management, there are instances where it may not fully resolve the issue, especially in cases of severe or chronic conditions. Some individuals may not achieve complete recovery or the same level of function as they had before the injury or condition. In such cases, physiotherapy may need to be supplemented with other treatments such as medication, injections, or, in some cases, surgery.
Additionally, physiotherapy results can vary from person to person. What works for one individual may not be as effective for another, and recovery time can differ greatly depending on the type and severity of the condition being treated.

4. Cost
While physiotherapy can be cost-effective in the long run by preventing further injuries or surgeries, the upfront cost of treatment can be a concern for some individuals, especially if sessions are not covered by insurance. Depending on where you live and the type of treatment required, the cost of physiotherapy sessions can add up quickly.
For individuals who require long-term treatment or multiple sessions per week, the financial burden may be significant. Some people may need to explore alternative options or seek financial assistance, such as insurance coverage or payment plans, to make treatment more affordable.
5. Limited Availability
Physiotherapy may not always be readily available, especially in rural or remote areas where there are fewer clinics or trained practitioners. For people in these locations, accessing regular physiotherapy sessions may be difficult, leading to delays in treatment. Additionally, some physiotherapy services may have long waitlists, particularly in high-demand areas, which can delay recovery and cause frustration.
In such cases, patients may need to explore telehealth or virtual physiotherapy options, though not all conditions may be adequately addressed through remote treatment.

6. Potential for Over-reliance on Physiotherapy
In some cases, individuals may develop an over-reliance on physiotherapy and become dependent on the therapist for continued care. While physiotherapy can provide invaluable support and recovery tools, it’s essential for patients to take an active role in their rehabilitation and follow through with exercises and lifestyle changes on their own.
An over-reliance on physiotherapy could result in less self-efficacy and hinder long-term health management. The goal of physiotherapy is to empower patients to manage their condition independently, but it requires active participation and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan.

7. Not a Quick Fix
Physiotherapy is not a quick-fix solution. Depending on the condition, it may take weeks or even months to see significant improvement. Patients seeking rapid results may find physiotherapy frustrating, particularly if they are not seeing immediate changes or if they have a high tolerance for pain and expect faster results.
Patience and consistency are essential in physiotherapy, and it may not be the ideal choice for individuals who are looking for instant relief.

Conclusion
Physiotherapy offers a wide range of benefits, including pain relief, improved mobility, injury prevention, and chronic condition management. It is a non-invasive and holistic treatment that helps patients regain function, improve posture, and achieve long-term health benefits. However, it also has some drawbacks, including potential discomfort during treatment, the time commitment involved, and the possibility of incomplete results.
Ultimately, the decision to pursue physiotherapy depends on the specific needs of the individual, the nature of the condition, and the desired outcome. When done correctly and consistently, physiotherapy can be an excellent way to improve both physical and mental well-being, but it is important to set realistic expectations and be aware of the limitations.










